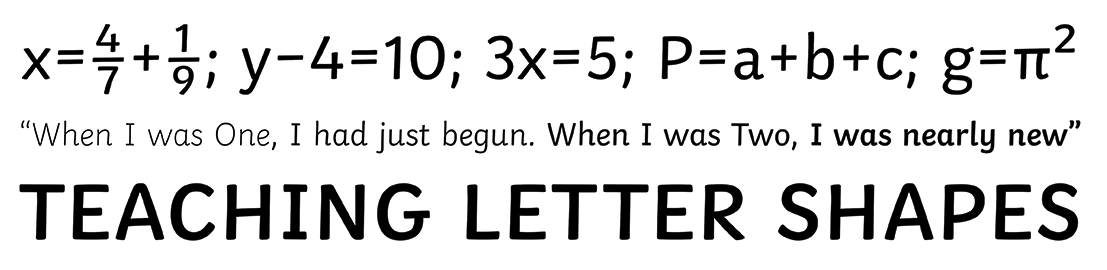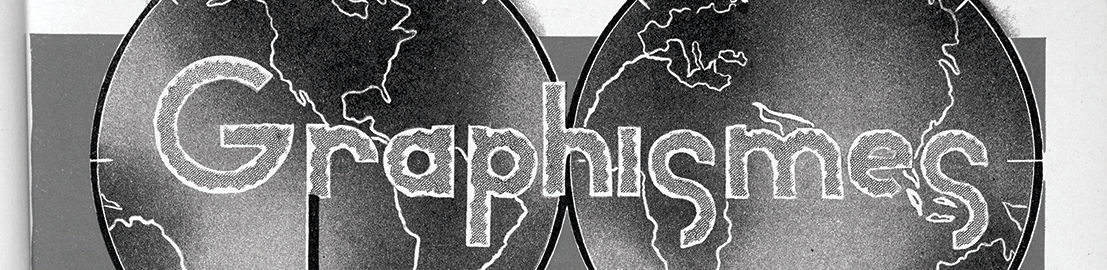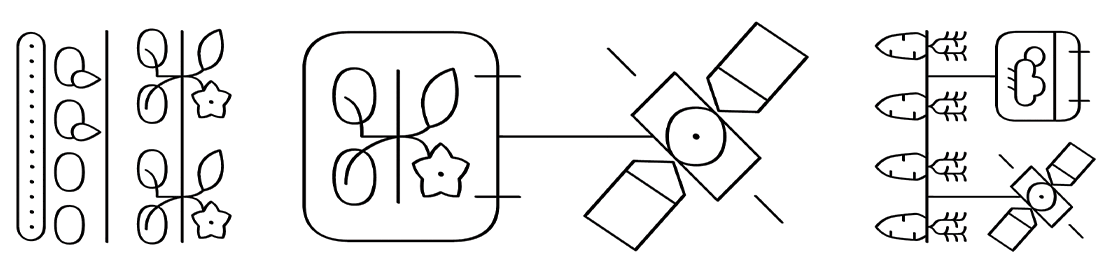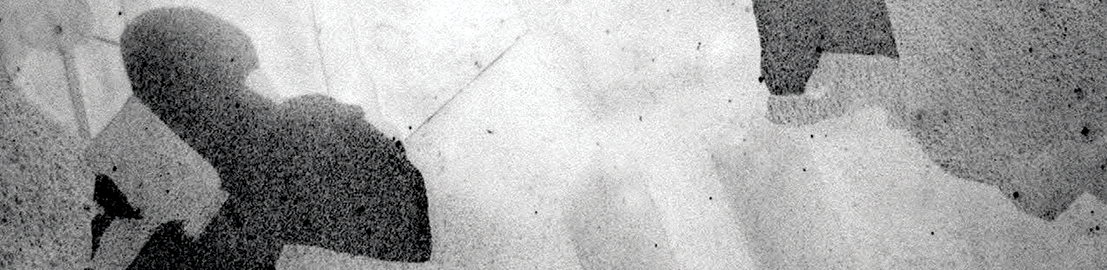The skeleton has been a key figure throughout the evolution of the animated image. Thisessay investigates how the danse macabre lies at the roots of animation, and has hence kepton reappearing as a motif throughout the evolution of the genre. The theoretical frameworkcombines film history with media-archeology and iconology. Ever since Athanasius Kircher’sfamous description of a magic lantern in the second edition of his publication Ars Magna luciset umbrae (1671), the image of a skeleton or the grim reaper has appeared time and again asthe key signifier in the process of animating (i.e., moving, resurrecting) still images. ChristiaanHuygens was, however, the first person to describe the projection of moving lantern images. Inhis notes of 1659 he included drawings, based on Holbein’s Dance of Death, of a skeleton toyingwith its own skull. As these optical instruments were also called ‘philosophical toys’, then theskeleton is the most appropriate motif, a memento mori in motion. Over the years the skeletonhas played a central role in phantasmagoric shows (an expanded media show orchestratedaround a hidden magic lantern), in the demonstration of the choreutoscope (an invention byL.S. Beale in 1866, and the first application of the Maltese cross for transporting film), and inmany early animation films such as fantasmagorie (Cohl) and skeleton dance (Disney). Fromits inception, animation has thus been used to illustrate acts of reanimation, bringing deadmatter back to life.

TMG – Journal for Media History
Vol 19, No.2 (2016)
‘Typography in Media Historical Perspective’
Gutenberg’s invention of movable type has played a vital role in modern history. The introduction of new (digital) media technologies seems to signal a second typographical revolution, which will change our conceptions and practices of reading, writing and publication of texts radically. Therefore new forms of ‘information’, reflection, and research are needed.
Ekaterina Zaitseva and Kemal Eroğlu developed this experimental online prototype for this special issue of TMG of which the official version can be found here. They also designed the typographic layout of the pdf versions of the articles. This experimental website is a prototype and therefore only partly functional, and some of the functions, such as the reference to other relevant issues of TMG are simulated with arbitrary references.
The editorial board would explicitly like to thank Ewan Lentjes for his invaluable contribution to this special issue as guest editor.
‘Typografie in mediahistorisch perspectief’
Gutenbergs uitvinding van de boekdruk heeft een cruciale rol gespeeld in de ontwikkeling van de moderne geschiedenis. Met de nieuwe-mediatechnologie lijkt een tweede typografische revolutie haar intrede te doen. Onze opvattingen over lezen, schrijven en publiceren veranderen radicaal. Nieuwe vormen van ‘informatie’, reflectie en onderzoek dienen zich aan.
Als onderdeel van hun eindexamenproject voor de afdeling Graphic Design (ArtEZ Arnhem) hebben Ekaterina Zaitseva en Kemal Eroğlu een experimentele online prototype voor dit themanummer van TMG ontwikkeld waarvan de officiële versie hier kan worden geraadpleegd. Ze hebben ook zorg gedragen voor de typografische vormgeving van de pdf versies van de artikelen.
Aangezien deze experimentale website een prototype is, zijn niet alle functies uitgewerkt en sommige (zoals bijvoorbeeld de referentie aan relevante andere artikelen) gesimuleerd met arbitraire verwijzingen.
De redactie bedankt Ewan Lentjes die als gastredacteur een substantiële bijdrage heeft geleverd aan de totstandkoming van dit nummer.
Colophon
Editor/redacteur: Jack Post
Guest Editor/gastredacteur: Ewan Lentjes
Editor-in-Chief/eindredacteur: Thunnis van Oort
Design/ontwerp: Ekaterina Zaitseva and Kemal Eroğlu
Coding (online version/versie): Bernd de Ridder
Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, Faculteit der Letteren
t.a.v. Tom Slootweg
Oude Boteringestraat 23
9712 GC Groningen
t.slootweg@rug.nl
Bas Agterberg
Publisher
Nederlands Instituut voor Beeld en Geluid
Postbus 1060
1200 BB Hilversum
Phone: +31 (0)35 6777062
Email: uitgevertmg@beeldengeluid.nl
Bas Agterberg
Phone: +31 (0)35 6777062
Email: uitgevertmg@beeldengeluid.nl